Compare Flask and web2py
Flask is a Python web framework for building web applications. It is based on Werkzeug and Jinja 2. It is a minimalist, 'no batteries included' framework. Yet it can be scaled extensively and support complex applications and use cases by adding required functionality as needed. It follows the philosophy that if something needs to be initialized, it should be initialized by the developer.
web2py was originally designed as a teaching tool, but it gained adoption outside of the academic world. It is a full-stack framework containing all the components needed to build fully functional web applications using the Model View Controller (MVC) pattern. Inspired by the Ruby on Rails and Django. It is not very popular right now but was ranked amongst top Python web frameworks in 2011.
Let's see how Flask and web2py compare on various factors and features and which to choose when.

Flask

web2py
Overall
Type
Release Date
Adoption and Ease of Use
Used by
Performance [?]


Flexibility


Ease of Learning

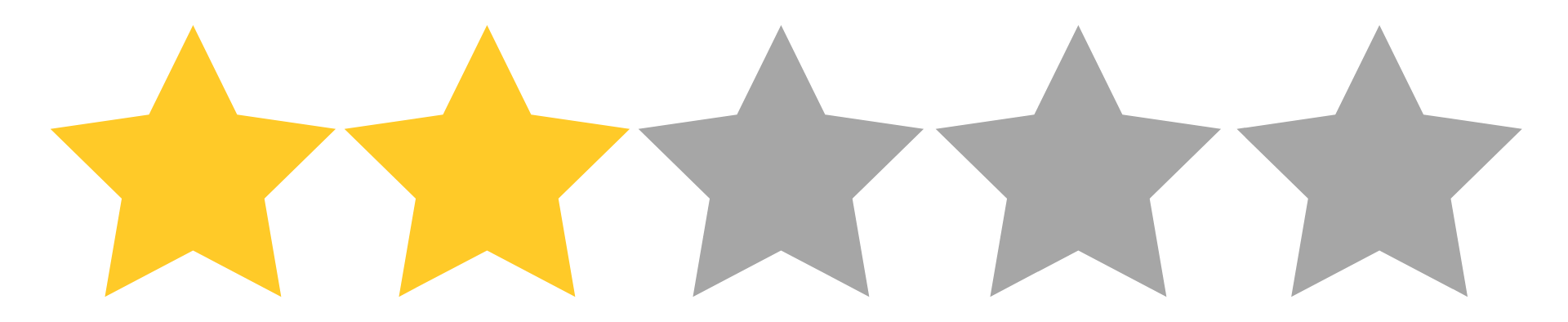
Database Support
RDBMS Support
NoSQL Support
Web & Core Features
Admin Dashboard
Security
Templating Library
Web Forms
Authentication
If you found this useful, please help us grow by sharing this article with your followers using the sharing icons. Every share or call out will help. Thank you.
Similar Comparisons
- Compare Bottle vs CherryPy
- Compare Bottle vs Fast API
- Compare Bottle vs web2py
- Compare Django vs Bottle
- Compare Django vs CherryPy
- Compare Django vs Fast API
- Compare Django vs Flask
- Compare Django vs Pyramid




Comments (1)
Mohammed
The most comprehensive comparison on the web. Thanks a lot. I have made my mind. Flask is the way to go.