Books / Introduction to Networking / Chapter 5
The Domain Name System
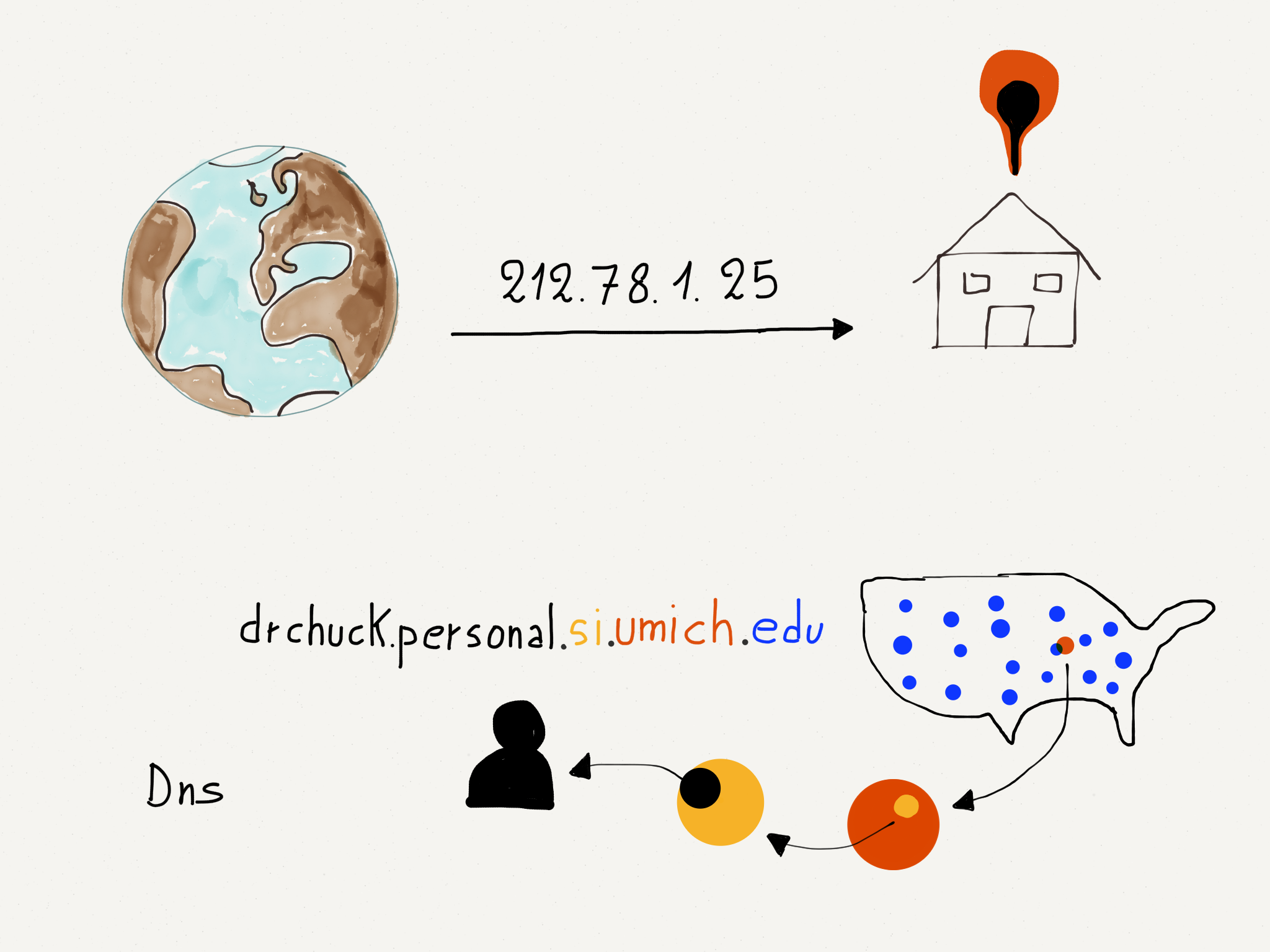
The Domain Name System lets you access websites by their domain name like (www.codeahoy.com), so you don’t have to keep a list of numeric Internet Protocol (IP) addresses like “212.78.1.25”. IP address are determined by where your computer connects to the Internet. When you have a portable computer and you move from one location to another, you get a new IP address at each new location. Since no one connects to your portable computer, it does not matter if your IP address changes from time to time. But since so many people connect to a web server, it would be inconvenient if the server moved to a new location and needed to change its IP address.
When your computer makes a connection to a system using a domain name address, the first thing your computer does is look up the IP address that corresponds to the domain name. Then your computer makes the connection using the IP address.
Adding the separate step of looking up the IP address for a DNS address also makes it easier to move a server from one location to another. The server is given a new IP address and the entry for the domain address is updated. Once the DNS entry is updated, new requests for the domain name are given the new IP address. Since end users access most servers using domain names and never see the IP address, a server can be moved to a new network connection without affecting the end user’s ability to access the server.
Allocating Domain Names
If you recall from the previous section, IP addresses are allocated based on where you connect a new network to the Internet. Domain names are allocated based on organizations that “own” the domain name. At the top of the domain name hierarchy is an organization called the International Corporation for Assigned Network Names and Numbers(ICANN). ICANN chooses the top-level domains (TLDs) like .com, .edu, and .org and assigns those to other organizations to manage. Recently a new set of TLDs like .club and .help have been made available.
ICANN also assigns two-letter country code top-level domain names like .us, .za, .nl, and .jp to countries around the world We call these Country-Code Top-Level Domain Names (ccTLDs). Countries often add second-level TLDs, like .co.uk for commercial organizations within the UK. Policies for applying for domain names with any particular ccTLD vary widely from one country to another.
Domain Names.
Once a domain name is assigned to an organization, the controlling organization is allowed to assign subdomains within the domain. As an example, the .edu top-level domain is assigned to the Educause organization. Educause assigns domains like umich.edu to higher education institutions. Once the University of Michigan is given control of umich.edu, it can make its own choices for subdomains within its new domain. Domains ending in .com and .org can be purchased by individuals. The individual owners of those domains are allowed to manage their domain and create subdomains under it for their own use or use by others.
Reading Domain Names
When we look at an IP address like “212.78.1.25”, the left prefix is the “Network Number”, so in a sense we read IP addresses from left to right, where the left part of the IP address is the most general part of the address and right part of the address is most specific:
212.78.1.25
Broad ----> Narrow
For domain names, we read from right to left:
drchuck.personal.si.umich.edu
Narrow <--- Broad
The most general part of this domain name is “.edu”, which means higher education institutions. The subdomain “umich.edu” is a particular higher education institution.
Summary
While the Domain Name System is not one of our four layers in the model, it is an important part of making the Internet easier to use. Domain names allow end users to use symbolic names for servers instead of numeric Internet Protocol addresses. By adding a service that maps domain names to IP addresses, we can move servers from one Internet connection to another connection without requiring users to manually change their configurations to connect to a server.
If you would like to purchase a domain name for yourself or your company, you can choose from any number of domain name registrars.
Glossary
DNS: Domain Name System. A system of protocols and servers that allow networked applications to look up domain names and retrieve the corresponding IP address for the domain name.
domain name: A name that is assigned within a top-level domain. For example, codeahoy.com is a domain that is assigned within the “.org” top-level domain.
ICANN: International Corporation for Assigned Network Names and Numbers. Assigns and manages the top-level domains for the Internet.
registrar: A company that can register, sell, and host domain names.
subdomain: A name that is created “below” a domain name. For example, “umich.edu” is a domain name and both “www.umich.edu” and “mail.umich.edu” are subdomains within “umich.edu”.
TLD: Top Level Domain. The rightmost portion of the domain name. Example TLDs include “.com”, “.org”, and “.ru”. Recently, new top-level domains like “.club” and “.help” were added.
Questions
- What does the Domain Name System accomplish?
- a)It allows network-connected computers to use a textual name for a computer and look up its IP address
- b)It keeps track of the GPS coordinates of all servers
- c)It allows Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) to manage IP addresses on the various continents
- d)It assigns different IP addresses to portable computers as they move from one WiFi to another
- What organization assigns top-level domains like “.com”, “.org”,
and “.club”?
- a)IANA - Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
- b)IETF - Internet Engineering Task Force
- c)ICANN - International Corporation for Assigned Network Names and Numbers
- d)IMAP - Internet Mapping Authorization Protocol
- Which of these is a domain address?
- a)0f:2a:b3:1f:b3:1a
- b)192.168.3.14
- c)www.khanacademy.org
- d)@drchuck
- Which of these is not something a domain owner can do with their domain?
- a)Create subdomains
- b)Sell subdomains
- c)Create new top-level domains
- d)Assign an IP address to the domain or subdomain