Books / Patterns for Beginning Programmers / Chapter 34
Checklists
In many aspects of life, both personal and professional, it is necessary to determine if a set of criteria have been satisfied/accomplished (e.g., goals have been reached, courses have been taken). One common way to do this is to use a checklist.
Motivation
Suppose you’re getting ready to go on vacation; you probably have a number of things that you want to remember to pack (e.g., shirts, socks, pants, and skirts). So, you decide to write a program to help you ensure that you don’t forget anything. However, unlike the situations considered in Chapter 12 on bit flags, the program will be provided with the checklist dynamically at run-time (i.e., it isn’t known when the program is written and compiled).
Review
To increase the flexibility of the program, you decide to represent the
criteria that need to be satisfied/accomplished as a String[] named
checklist, and you populate that array before you start working on the
tasks. Then, as you accomplish a task, you enter it into another
String[] named accomplished. Each time you accomplish a task you
want to be able to determine whether or not you are done (e.g., whether
you have completed all of the tasks in the checklist).
Of course, it’s easy to compare a single element of checklist with a
single element of accomplished using the equals() method in the
String class. However, in and of itself, that doesn’t solve the
problem of determining whether or not you are done. Clearly, the
equals() method must be invoked iteratively.
Thinking About The Problem
You can determine whether any given element of checklist has been
accomplished by comparing it with each element in accomplished. For
example, you can determine whether element index of checklist has
been accomplished as follows:
boolean done = false;
for (int a = 0; a < accomplished.length; a++) {
if (accomplished[a].equals(checklist[index])) {
done = true;
break;
}
}
At the end of this loop, done will contain true if and only if
checklist[index] has been accomplished.
This loop can be used to determine whether a single criterion has been satisfied/accomplished. To determine if all of the criteria have been satisfied/accomplished this loop needs to be nested inside of another loop. Unfortunately, there are many ways to do this incorrectly.
For example, the following implementation returns false at the first
discrepancy between the two arrays, which may just be a result of a
difference in how the two are ordered:
for all elements in accomplished {
for all elements in checklist {
if the accomplished element does not equal the checklist element {
return false
}
}
}
return true
As another example, the following implementation returns true as soon
as it determines that one item on the checklist has been accomplished:
for all elements in accomplished {
assign false to the accumulator named checked
for all elements in checklist {
if the accomplished element equals the checklist element {
assign true to the accumulator named checked
break
}
}
if checked is true then return true
}
return false
In short, there are many incorrect ways to think about the problem. To
get the right answer, you must think carefully about the way the loops
are nested, the Boolean expression in the if statement, the way in
which break statements are used, and where return statements are
located.
The Pattern
For this problem, there are two variants of the pattern. In the first
variant, you only want the method to return true when all of the items
on the checklist have been accomplished. You can solve this variant with
a single boolean accumulator as follows:
private static boolean checkFor(String[] checklist, String[] accomplished) {
boolean checked;
for (int c = 0; c < checklist.length; c++) {
checked = false;
for (int a = 0; a < accomplished.length; a++) {
if (checklist[c].equals(accomplished[a])) {
checked = true;
break;
}
}
if (!checked) return false; // An item was not accomplished
}
return true; // All items were accomplished
}
Note that this algorithm breaks out of the inner loop as soon as it
determines that the checklist item of interest has been accomplished. It
returns false as soon as it determines that any checklist item was not
satisfied/accomplished. Hence, if both loops terminate normally then all
of the items on the checklist must have been accomplished and the method
returns true.
In the second variant of the pattern, you want the method to return
true when more than needed elements of the checklist have been
accomplished. For this variant, you can use an int accumulator named
count that keeps track of the number of items on the checklist that
have been accomplished, as follows:
private static boolean checkFor(String[] checklist, String[] accomplished,
int needed) {
int count;
count = 0;
for (int c = 0; c < checklist.length; c++) {
for (int a = 0; a < accomplished.length; a++) {
if (checklist[c].equals(accomplished[a])) {
++count;
if (count >= needed) return true;
else break;
}
}
}
return false; // Not enough items were accomplished
}
Again, this algorithm can break out of the inner loop when it determines
that the checklist item of interest has been accomplished. In addition,
it can return early when count reaches needed. However, in this
case, an early return means the checklist has been
satisfied/accomplished. Hence, if both loops terminate normally then the
method returns false.
Note that both implementations could be improved by checking to ensure
that accomplished.length is at least as large is necessary to
satisfy/accomplish the checklist (i.e., at least as large as
checklist.length in the first variant and at least as large as
needed in the second variant). This improvement was omitted for the
sake of simplicity.
Examples
It is useful at this point to consider some examples involving both
variants above. In all of these examples, checklist contains the
elements "Shirts", "Socks", "Pants", and "Skirts".
The Inflexible Variant
First, suppose that accomplished contains the elements "Shirts",
"Socks", "Pants", "Dresses", and "Shoes". In outer iteration 0,
the method checks to see if "Shirts" has been accomplished. In inner
iteration 0, the method determines that it has been and breaks out of
the inner loop. In outer iteration 1, the method checks to see if
"Socks" has been accomplished. In inner iteration 0, the method
determines that it hasn’t been, but in inner iteration 1 it determines
that it has been and breaks out of the inner loop. The iterations then
continue as follows:
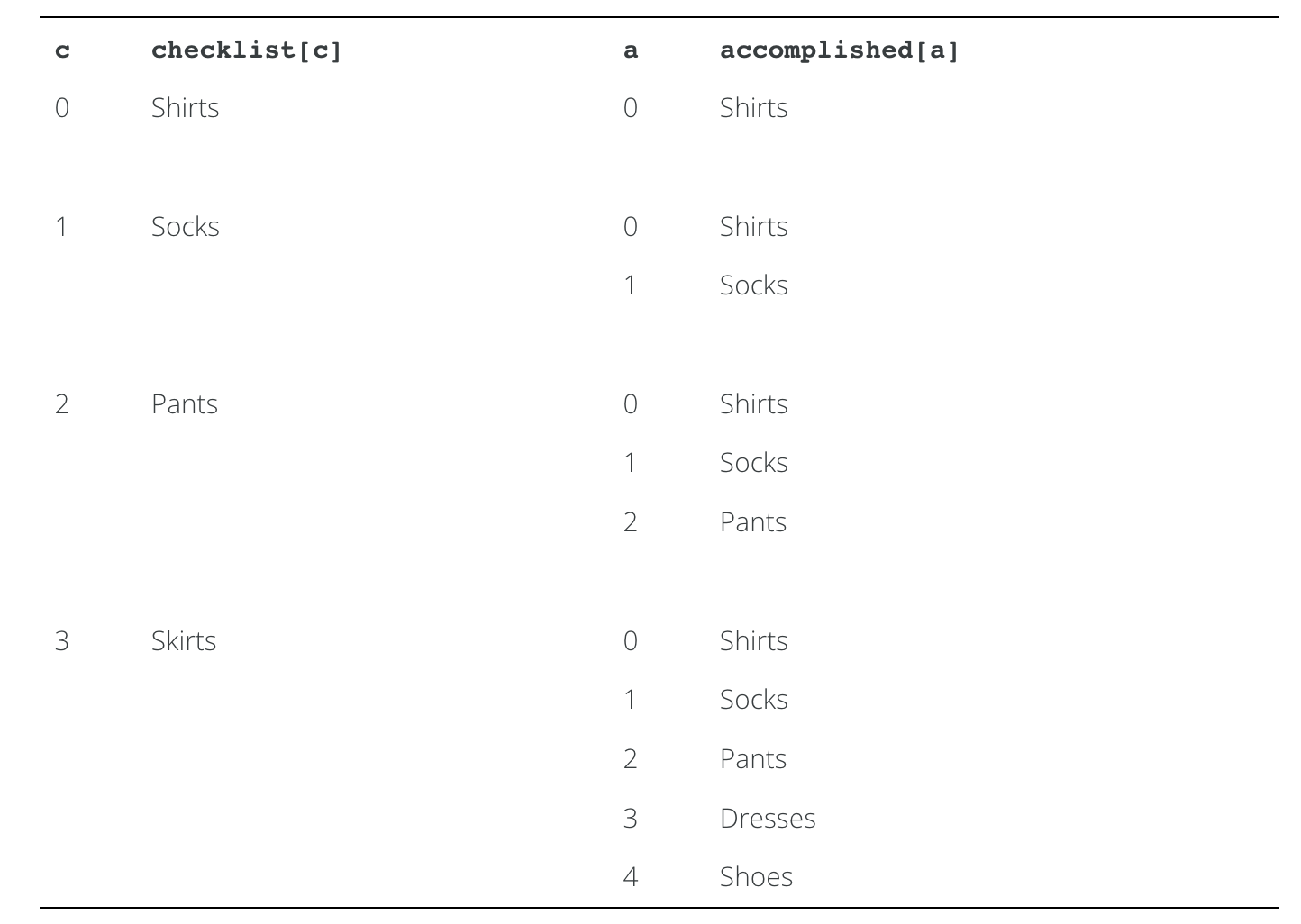
Since checklist[3] is not an element of accomplished, the local
variable checked is never assigned the value true, and the method
returns false.
Now, suppose that accomplished contains the elements "Socks",
"Shirts", "Skirts", and "Pants". In outer iteration 0, the method
checks to see if "Shirts" has been accomplished. In inner iteration 0,
the method determines that it hasn’t been, but in inner iteration 1 it
determines that it has and breaks out of the inner loop. In outer
iteration 1, the method checks to see if "Socks" has been
accomplished. In inner iteration 0, the method sees that it has been and
breaks out of the inner loop. The iterations then continue as follows:
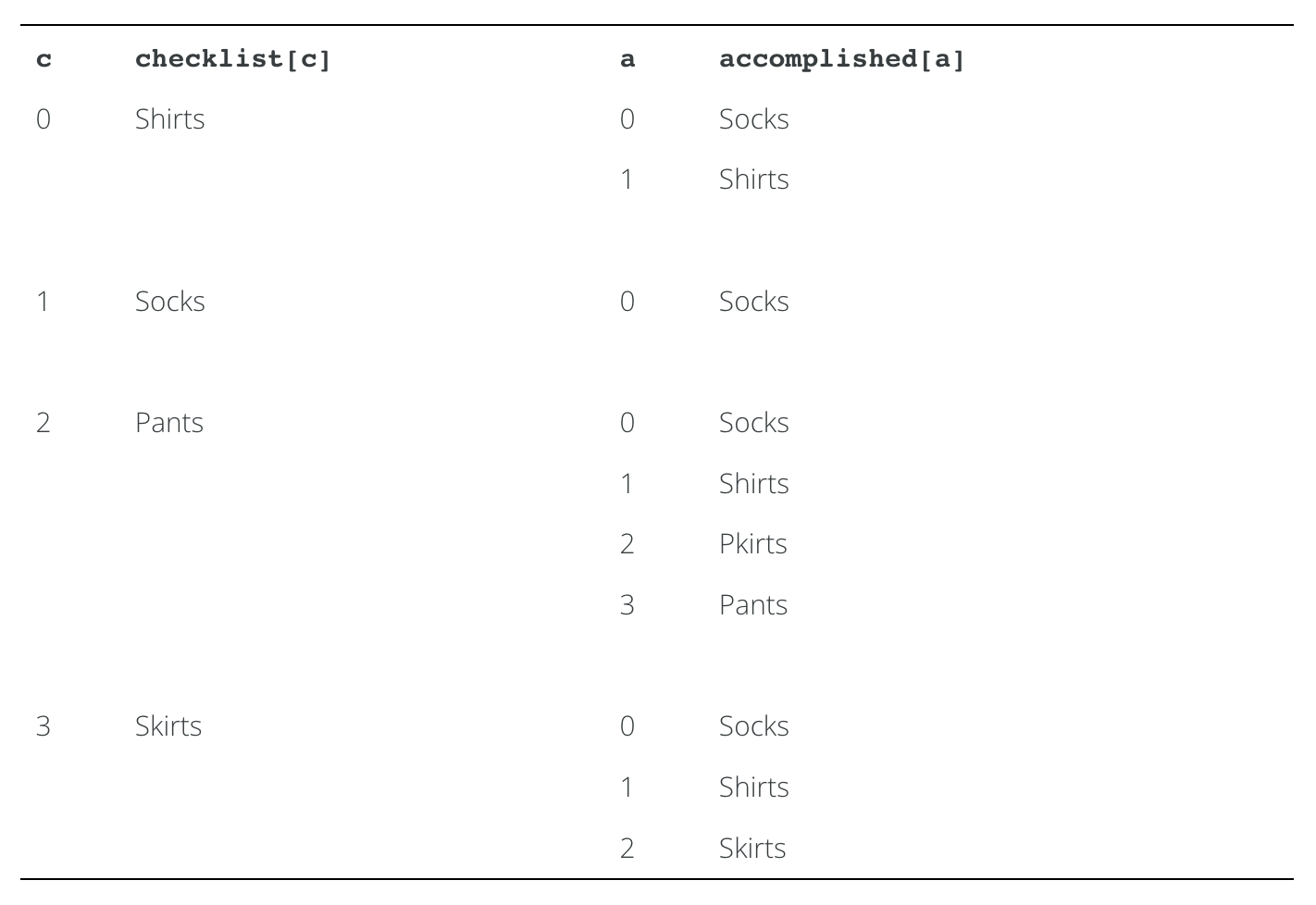
In this case, checked is assigned the value true in every outer
iteration, and the method returns true.
The Flexible Variant
Now consider the first example above but with the second variant of the
method, when 2 is passed into the formal parameter named needed
(because, apparently, this person is fully-dressed when wearing any two
items in the checklist). In outer iteration 0, the method checks to see
if "Shirts" has been accomplished. In inner iteration 0, the method
determines that it has been, increases count to 1, and breaks out of
the inner loop. In outer iteration 1, the method checks to see if
"Socks" has been accomplished. In inner iteration 0, the method
determines that it hasn’t been, but in inner iteration 1 it determines
that it has been, increases count to 2, determines that count is
greater than or equal to needed, and returns true.
Now, consider an example in which accomplished contains the elements
"Dresses" and "Shirts". These iterations will proceed as follows:
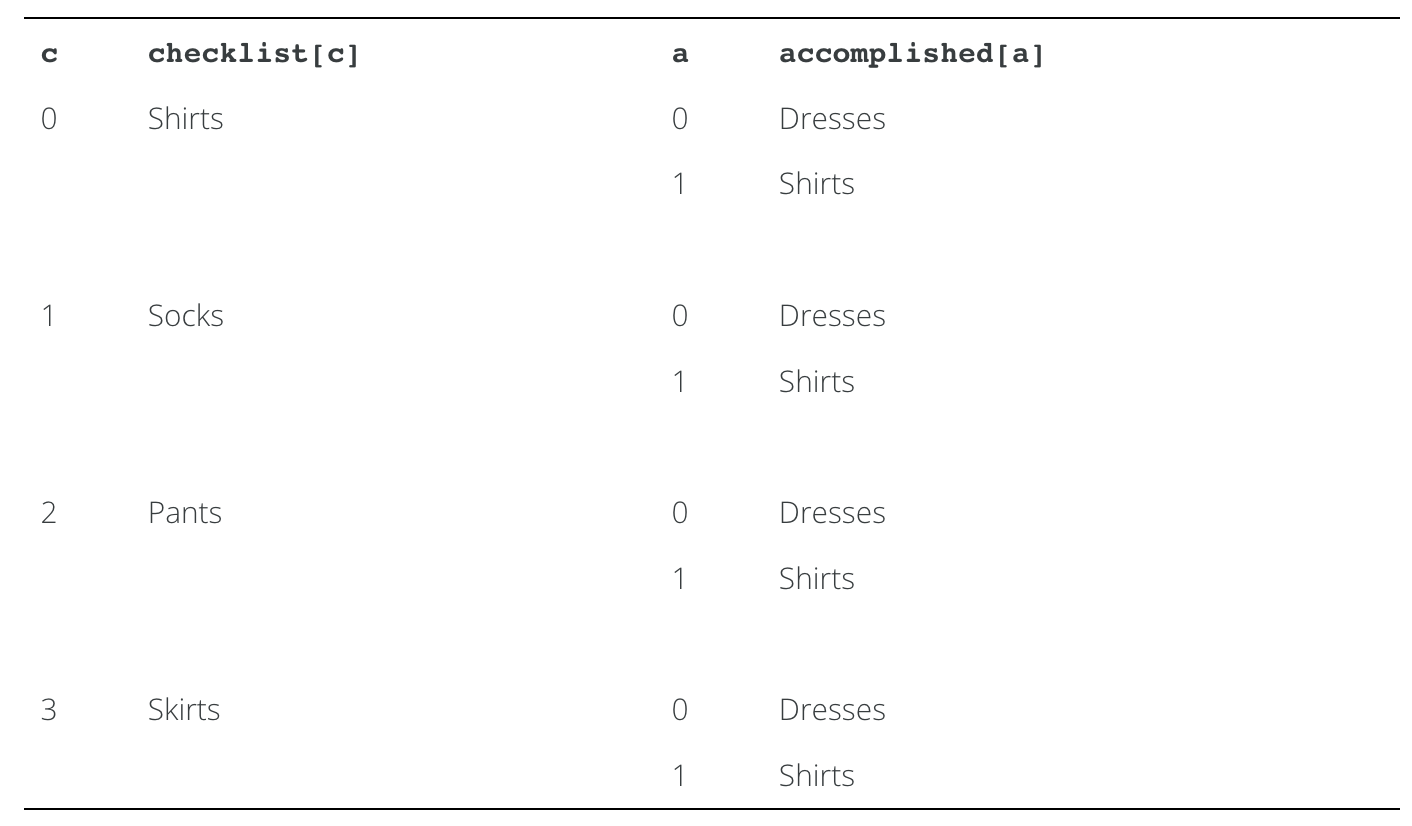
In inner iteration 1 of outer iteration 0 the method determines that
"Shirts" have been packed, and increases count to 1. However, none
of the inner iterations for outer iteration 1 correspond to "Socks",
none of the inner iterations for outer iteration 2 correspond to
"Pants", and none of the inner iterations for outer iteration 3
correspond to "Skirts". So, count is never increased to 2, and the
method returns false.
Looking Ahead
Though some thought was given to the efficiency of the algorithms above,
many issues were ignored, and none were considered formally. If you take
a course on data structures and algorithms, you will consider these
kinds of issues in detail. For example, it is interesting to ask whether
it is better to sort checklist and/or accomplished, either partially
or completely. It is also interesting to ask whether it is possible to
create a more efficient algorithm when the checklist consists of
sequential integers.