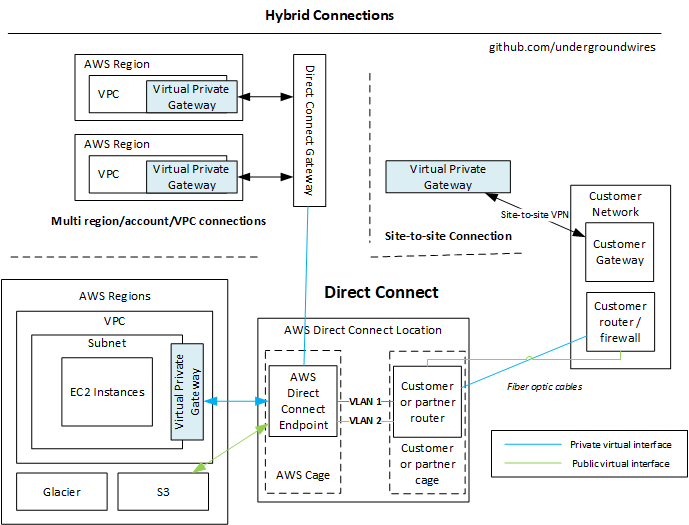
Networking - Hybrid connections
Site to site VPN
- Allows customer site (corporate network) to seamlessly communicate with AWS VPN as it’s in the same network
- Links Virtual Private Gateway from AWS side to Customer Gateway from customer side.
- Virtual Private Gateway (VPG)
- Deployed on VPC level (not subnet).
- Allows AWS to provide connectivity from AWS to other networks via VPN or Direct Connect.
- AWS requires Customer Gateway (CGW) on the customer side to connect to AWS VPC
- VPN concentrator on the AWS side of the VPN connection
- Created and attached to the VPC from which you want to create the Site-to-Site VPN connection
- Possibility to customize the ASN
- ASN = autonomous system number
- A unique number that’s available globally to identify an autonomous system and which enables that system to exchange exterior routing information with other neighboring autonomous systems.
- Internet = network of networks
- Routing is done through cooperation of autonomous systems (AS)
- Each AS cooperate to route the traffic to destination
- Each AS does routing within AS, then across AS and when it reaches destination, routing is done by the destination AS
- Different ISPs communicate through Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a standardized exterior gateway protocol designed to exchange routing and reachability information among autonomous systems
- Customer Gateway
- Software application or physical device on customer side of the VPN connection
- 📝 IP Address:
- Use static, internet-routable IP address for your customer gateway device
- If behind a CGW behind NAT, use the public IP address of the NAT instead of the public IP of the gateway
- ❗📝 You need to allow Route propagation on VPC
- Route propagation allows VPC to find your internal site in Site-to-Site connection.
- Routes representing your Site-to-Site VPN connection automatically appear as propagated routes in your route table.
- Flow
- Set-up customer gateway on-premises with your device/software
- Create customer gateway in AWS
- Set-up Virtual Private Gateway
- You can choose amazon default ASN (dynamic: BGP ASN) or custom ASN (static)
- Add private network in route table and enable route propagation.
- Create Site-to-Site VPN connection between gateways
Direct Connect
- Provides a dedicated private connection from a remote network to your VPC.
- Uses AWS Direct Connect links (fiber cables) from your Data Center to Direct Connect locations.
- You need to setup a Virtual Private Gateway on your VPC
- Access public resources (S3) and private (EC2) on same connection
- Accesses all AZs within a region
- 💡 Use cases:
- Increase bandwidth throughput
- E.g. working with large data sets and want lower cost on bandwidth
- More consistent network experience
- E.g. you experience shutdown & data loss
- E.g. you need to have applications using real-time data feeds
- Hybrid environments (on-prem + cloud)
- Supports both IPv4 and IPv6
- If you want to setup a Direct Connect to one or more VPC in many different regions (same account), you must use a Direct Connect Gateway
- Direct Connect Gateway
- Allows multi region, multi account and multi VPN connections
- 📝Does not peer, it allows between VPC and customer network
- VPN as back-up
- Use same VPG for both Direct Connect and VPN connection
- IP configurations
- For BGP in VPN => Advertise the same prefix for Direct Connect and the VPN.
- Static VPN => Add the same static prefixes to the VPN connection
- If same routes advertised: Direct connect path will always be preferred.
Licenses and Attributions
Copyright (C) CodeAhoy. This content is licensed under CC-BY-SA-4.0 license.
Original Content License
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International