High Availability - Disaster Recovery
- Disaster Recovery (DR) is about preparing for and recovering from a disaster
- Disaster: events that have negative impact on business continuity or finances
- Recovery types to cloud:
- On-premise => On-premise: Traditional DR, very expensive
- On-premise => Cloud: Hybrid recovery
- Cloud => Cloud: e.g. AWS Cloud Region A => AWS Cloud Region B
- 📝Terminology
- RPO: Recovery Point Objective
- The amount of data loss you’re willing to accept
- Based on:
- How back in time you can recover
- How often you take back-up
- RTO: Recovery Time Objective
- Amount of downtime you’re willing to accept
- Disaster Recovery Strategies
- From business continuity to uninterrupted business:
- Backup and Restore -> Pilot Light -> Warm / Hot Standby -> Hot Site / Multi Site
- Backup and Restore
- Cheapest option, slowest RTO.
- Take frequent snapshots of your data:
- from e.g. EBS Volumes, RDS databases, EC2 AMI’s
- to e.g. S3
- AWS Storage Gateway enables from on-premises to cloud back-up seamlessly
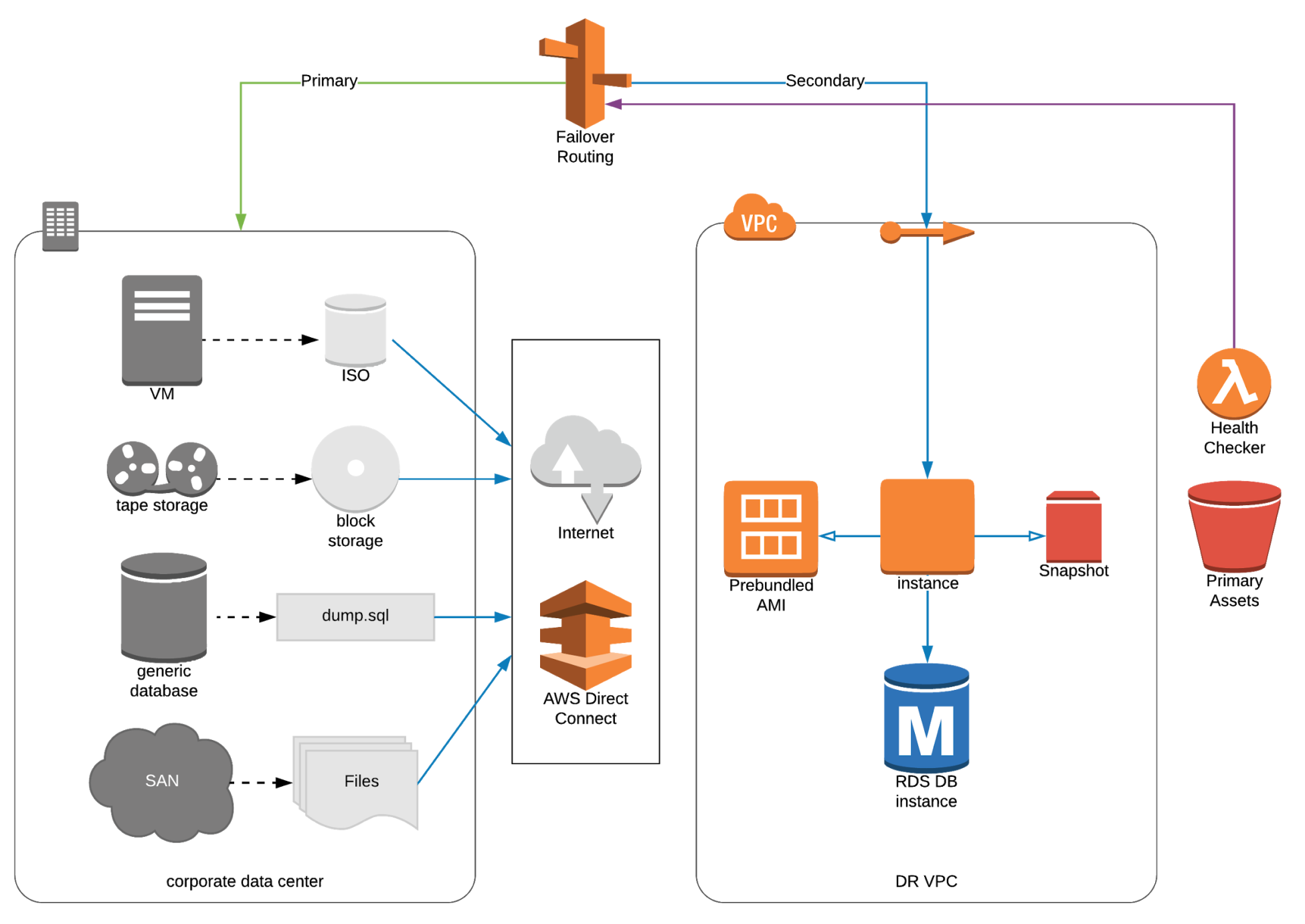
- Pilot Light
- Critical core element(s) of the app is always running in the cloud
- Faster than Backup and Restore as critical systems are already up.
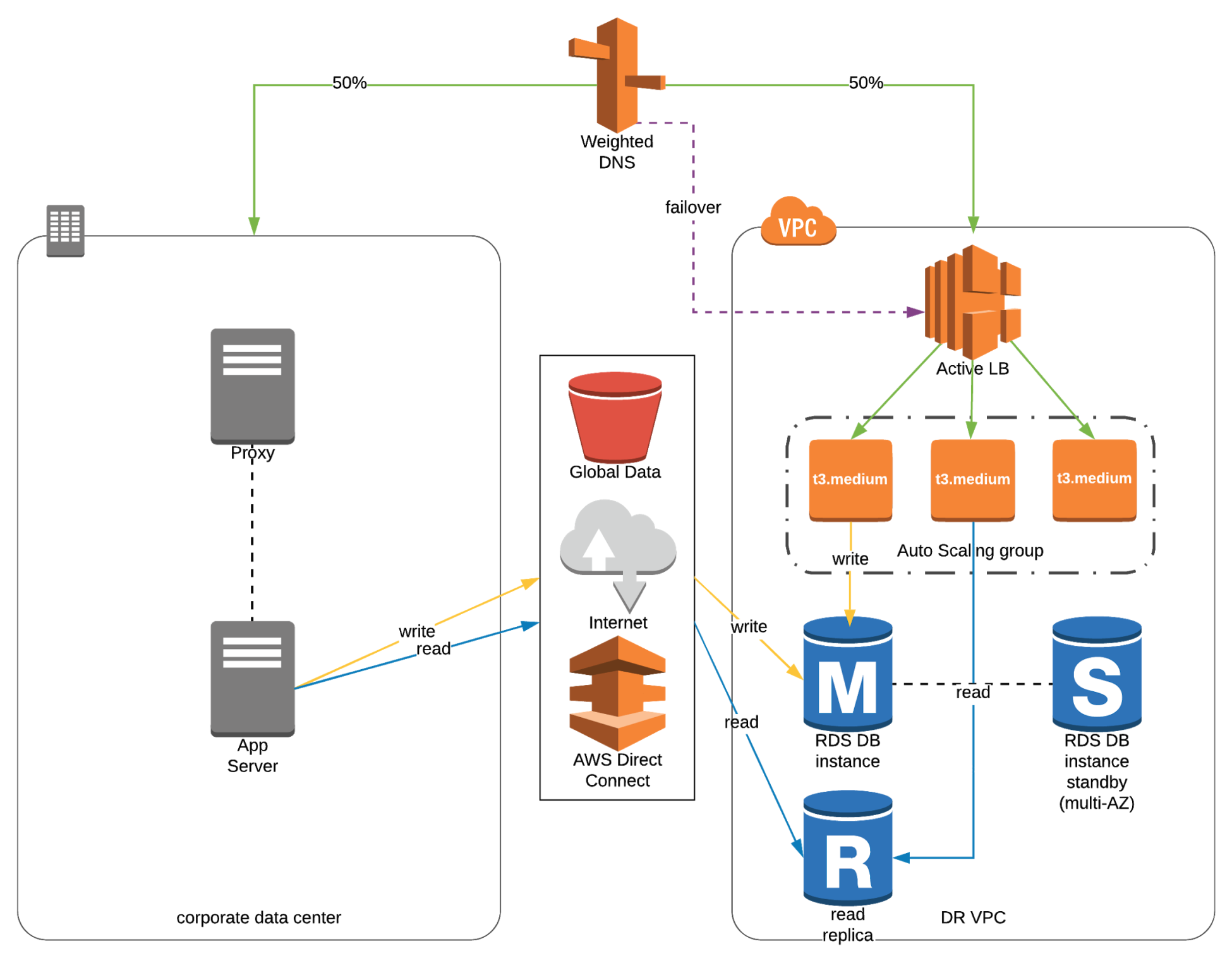
- Example of active/passive failover configuration.
- From networking, you have two options: Elastic IP addresses or Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
- DNS records to point to EC2 or point to LB using CNAME.
- Changed data in DR site after failover must be reversed back to primary site after failback.
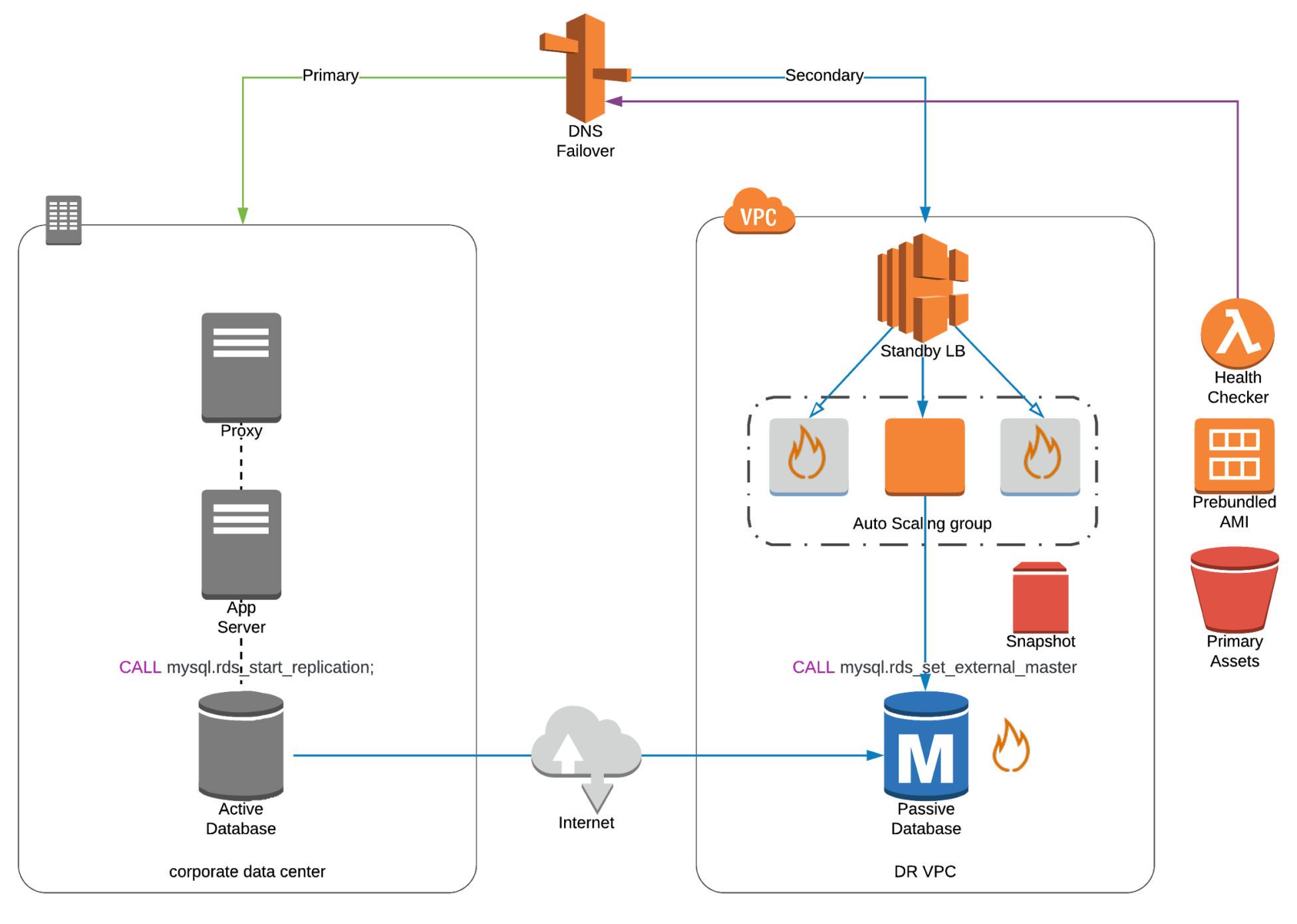
- Warm / Hot Standby
- Scaled-down full production environment always running in the cloud.
- Upon disaster, we can scale to production load
- Example of active/passive failover configuration.
- Changed data in DR site after failover must be reversed back to primary site after failback.
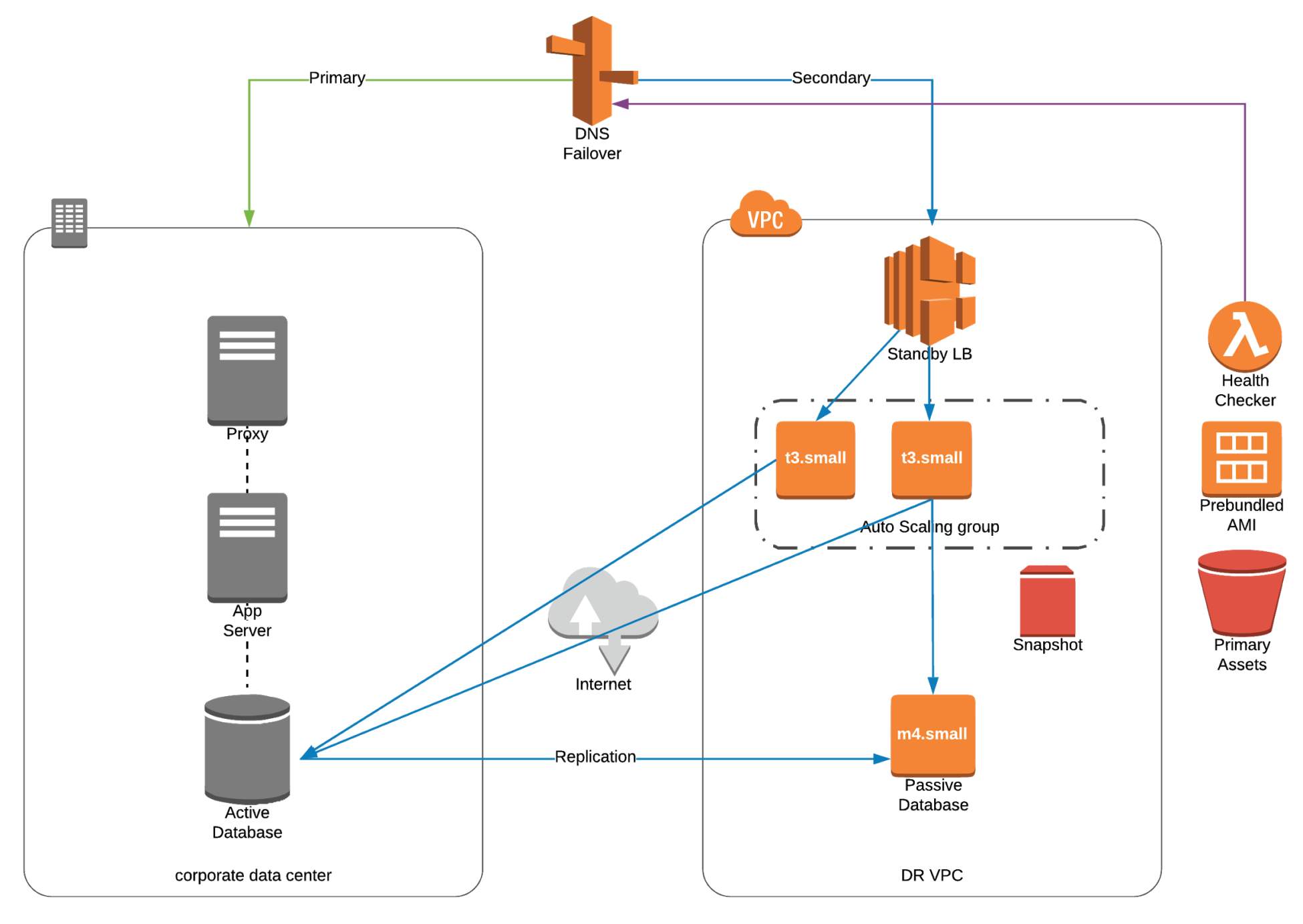
- Hot Site / Multi Site
- Full Production Scale is running AWS and on-premise
- Example of active-active failover configuration.
- Changed data in DR site after failover must be reversed back to primary site after failback.
- 💡 In Route 53: You configure active-active failover using any routing policy (or combination of routing policies) other than failover.
- 💡 Disaster Recovery Tips
- Backup
- EBS Snapshots, RDS automated backups / Snapshots, etc…
- Regular pushes to S3 / S3 IA / Glacier, Lifecycle Policy, Cross Region Replication
- From On-premise: Snowball or Storage Gateway
- High Availability
- Use Route 53 to migrate DNS over from Region to Region
- RDS Multi-AZ, ElastiCache Multi-AZ, EFS, S3
- Site to Site VPN As a recovery from Direct Connect
- Replication
- RDS Replication (Cross Region), AWS Aurora + Global Databases
- Database replication from on-premise to RDS
- Storage Gateway
- Automation
- CloudFormation / Elastic Beanstalk to re-create a whole new environment
- Recover / Reboot EC2 instances with CloudWatch if alarms fail
- AWS Lambda functions for customized automations
- 🤗 Chaos
- Netflix has a “simian-army” randomly terminating EC2.
- Chaos monkeys terminates instances in production.
Licenses and Attributions
Copyright (C) CodeAhoy. This content is licensed under CC-BY-SA-4.0 license.
Original Content License
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International