Books / AWS in Bullet Points - Exam Prep Study Notes / Chapter 18
High Availability and Scalability
Scalability
- Application / system can handle greater loads by adapting
- Scalability is linked but different to high availability
- Elasticity
- System can adapt to workload changes by provisioning and de-provisioning resources automatically to match current demand as closely as possible.
- Two kinds of scalability
- Vertical Scalability: scale up & down
- Increasing the size of the instance e.g. from
t2.microtot2.large - Common use case
- Distributed systems, such as database
- RDS, ElastiCache can scale vertically
- Hardware limits how much you can scale
- Increasing the size of the instance e.g. from
- Horizontal Scalability (= elasticity): scale in & out
- Increase number of instances / systems for application
- Common for web applications / modern applications
- Easy with e.g. Amazon EC2 through right-clicking
- For EC2, you can use Auto Scaling Groups or Load Balancers for horizontal scaling
- Vertical Scalability: scale up & down
High Availability
- Goes hand in hand with horizontal scaling
- Running application in at least 2 data centers (= Availability Zones)
- Goal is to survive a data center loss
- Can be:
- Passive e.g. RDS Multi AZ
- Active e.g. for horizontal scaling
- For EC2, you can use Auto Scaling Group with multi AZ enabled and Load Balancer with multi AZ enabled.
- 💡 Design for failure as it can happen
- 🤗 Netflix has simian army (monkeys) to inject failure into their production systems.
- E.g.
- Chaos Monkey => Terminate random EC2 instances
- Chaos Gorilla => Delete entire AZ
- Latency Monkey => introduces latency.
- and more…
- E.g.
- 🤗 Netflix has simian army (monkeys) to inject failure into their production systems.
Common architectures
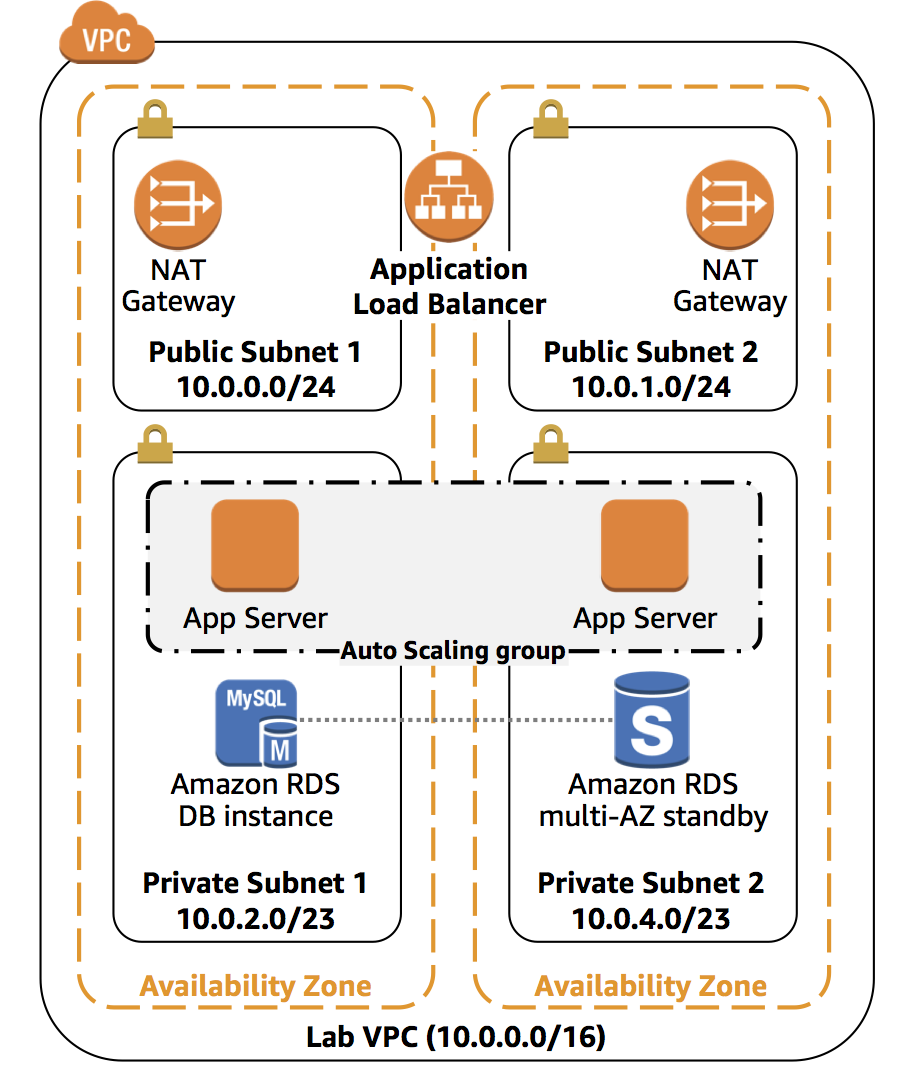
- Single region HA architecture
-
3 tier application with 3 tiered security
Tier Role Example service Security Group 1 Client Application Load Balancer Allow HTTP + HTTPs 2 Application Application servers (EC2) Allow HTTP from Client 3 Database Amazon RDS Allow e.g. MySQL from application SG - In a single VPC
- At least 2 AZ and and in each AZ:
- A public subnet and in each public subnet:
- Deploy NAT gateway
- Load balance public subnet in AZs through application load balancer
- A private subnet and in each private subnet:
- Deploy application server in same auto-scaling group
- Create route table that routes internet (0.0.0.0/0) to the NAT gateway of a public subnet in same AZ
- Configure auto-scaling group to put servers in public Load balancer
- Deploy RDS instance in one, and RDS multi-AZ standby in other one
- A public subnet and in each public subnet:
- At least 2 AZ and and in each AZ:
- 📝 E.g. if you have minimum 6 instances running and can tolerate failure of 1 AZ failure:
- Deploy 3 AZ with 3 instances in each AZ so you always have 6 instances running.
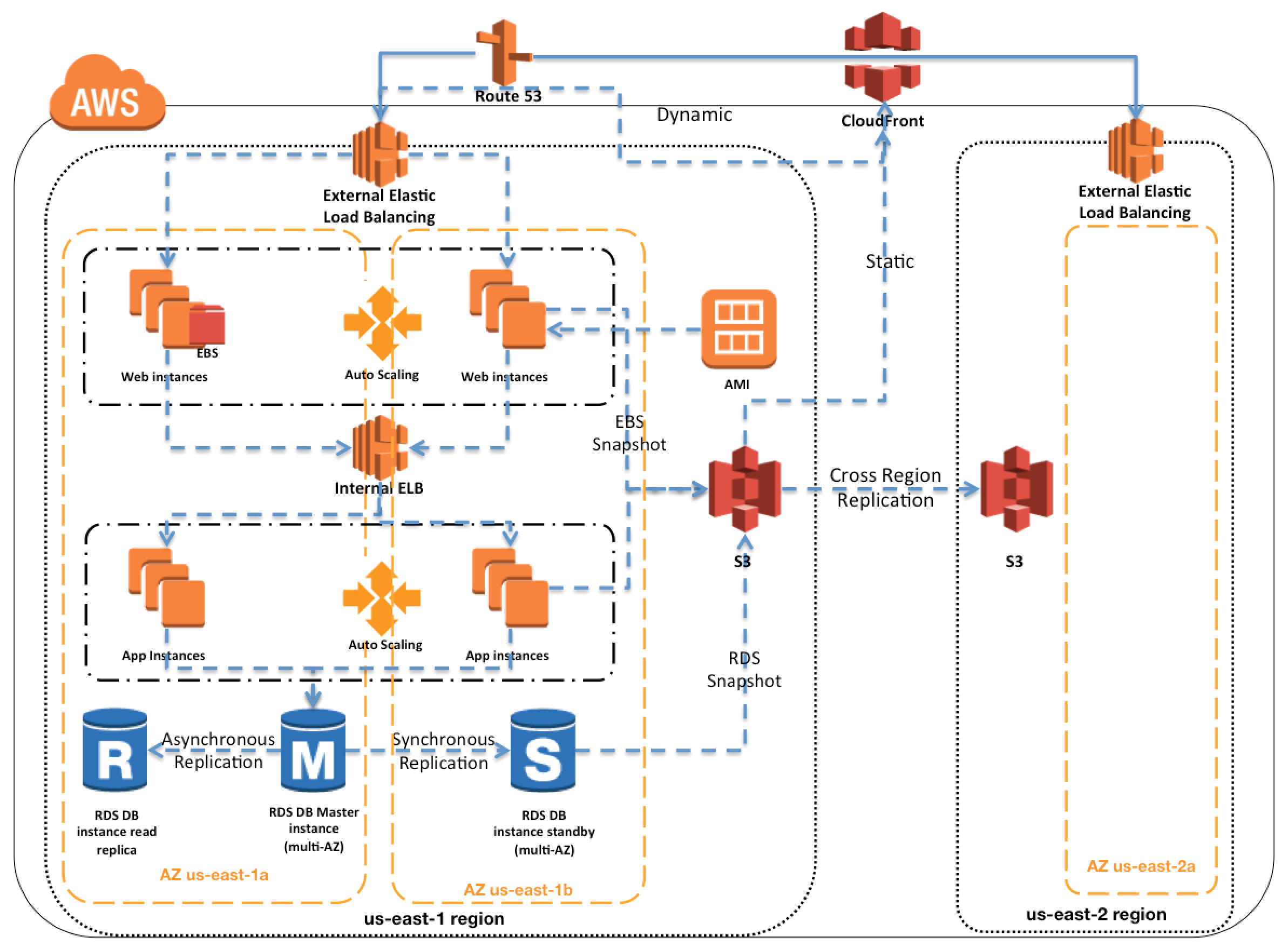
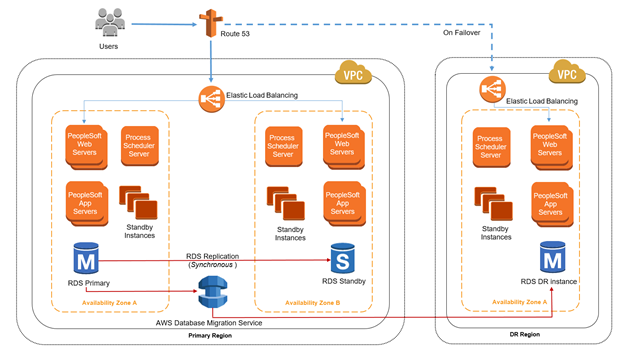
- Multi region HA architecture
- E.g. using S3
- E.g. using RDS
- E.g. using S3